Dr. Arindam Ghosh Gastro Intestinal Surgeon SGH DUBAI,UAE has a vast expertise and experience in gastric surgeries.He has performed 400 plus gastro esophageal surgeries
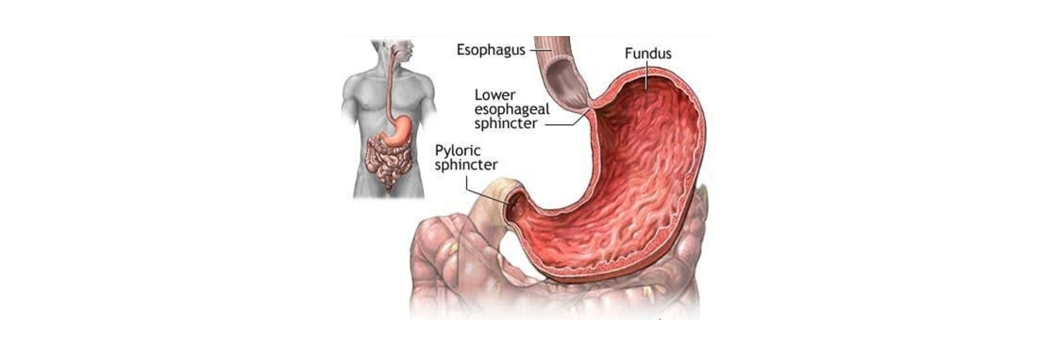
Stomach cancer occurs when cancerous cells form in the stomach lining.This type of cancer usually doesn’t cause symptoms until the later stages, so it’s often not diagnosed until it’s more advanced.While difficult to detect, treatment for stomach cancer is possible through chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and surgery.
Adenocarcinoma
About 90% to 95% of cancers of the stomach are adenocarcinomas. When the term stomach cancer or gastric canceris used, it almost always refers to an adenocarcinoma. These cancers develop from the cells that form the innermost lining of the stomach (known as the mucosa).
Lymphoma
These are cancers of the immune system tissue that are sometimes found in the wall of the stomach. About 4% of stomach cancers are lymphomas. The treatment and outlook depend on the type of lymphoma. For more detailed information, see Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma.
Gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST)
These are rare tumors that start in very early forms of cells in the wall of the stomach called interstitial cells of Cajal. Some of these tumors are non-cancerous (benign); others are cancerous. Although GISTs can be found anywhere in the digestive tract, most are found in the stomach. For more information, see Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST).
Carcinoid tumor
These are tumors that start in hormone-making cells of the stomach. Most of these tumors do not spread to other organs. About 3% of stomach cancers are carcinoid tumors. These tumors are discussed in more detail in Gastrointestinal Carcinoid Tumors.
Other cancers
Other types of cancer, such as squamous cell carcinoma, small cell carcinoma, and leiomyosarcoma, can also start in the stomach, but these cancers are very rare.
Risk Factors of Stomach Cancer
Stomach cancer is directly linked to tumors in the stomach. However, there are some factors that might increase your risk of developing these cancerous cells. These risk factors include certain diseases and conditions, such as:
lymphoma (a group of blood cancers)
H. pylori bacterial infections (a common stomach infection that can sometimes lead to ulcers)
tumors in other parts of the digestive system
stomach polyps (abnormal growths of tissue that form on the lining of the stomach)
nausia vomitting
frequent heartburn
loss of appetite (sometimes accompanied by sudden weight loss)
constant bloating
early satiety (feeling full after eating only a small amount)
bloody stools
anaemia