CAUSES OF GALLSTONE FORMATION
- Too Much Cholesterol in Your Bile
Composition of Bile: Bile is a digestive fluid produced by your liver that contains cholesterol, bile salts, and bilirubin.
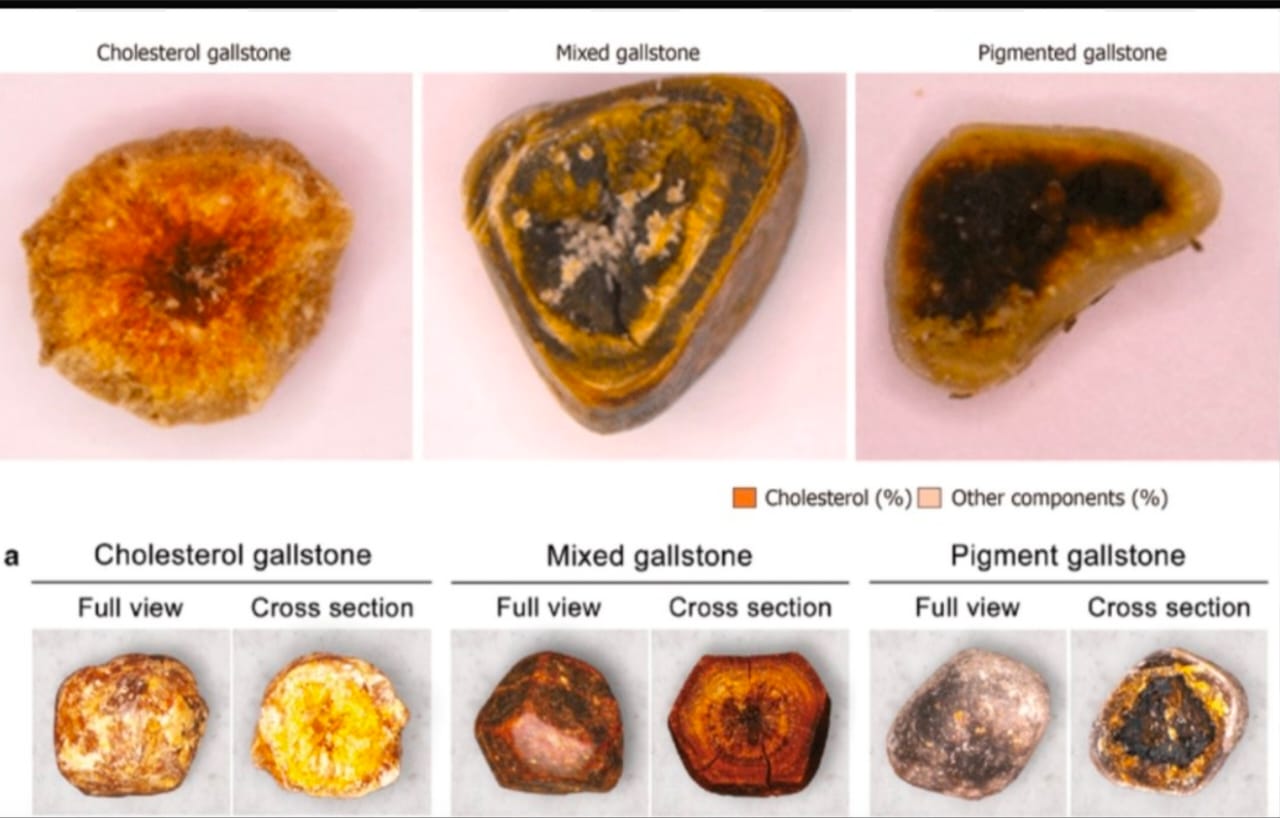
Cholesterol Saturation: If your liver excretes more cholesterol than your bile salts can dissolve, the excess cholesterol can crystallize and eventually form stones. This is the most common cause of gallstones, particularly “cholesterol stones.”
Factors Contributing to High Cholesterol:
Obesity: Being overweight or obese is a significant risk factor, as it can lead to increased cholesterol production and excretion.
Diet: A diet high in saturated fats and cholesterol can contribute to elevated cholesterol levels.
Rapid Weight Loss: Significant weight loss, especially through very low-calorie diets or bariatric surgery, can cause the liver to release more cholesterol into the bile.
- Too Much Bilirubin in Your Bile
Bilirubin: This is a chemical produced when red blood cells break down.
Pigment Gallstones: If your bile contains too much bilirubin, it can also crystallize and form stones. These are known as “pigment stones.”
Conditions Leading to Excess Bilirubin
– Liver Diseases: Conditions like cirrhosis (scarring of the liver) can affect bile composition and increase bilirubin levels.
– Blood Disorders: Certain conditions that cause increased breakdown of red blood cells (hemolytic anemias) can lead to pigment gallstones.
– Biliary Tract Infections: Infections in the bile ducts can also contribute to pigment stone formation.
- Gallbladder Not Emptying Correctly (Bile Stasis)Impaired Gallbladder Function:
If your gallbladder doesn’t empty properly or as frequently as it should, bile can become concentrated. This concentration can lead to the components of bile (cholesterol and bilirubin) crystallizing.
Other Risk Factors
- Age: The risk of developing gallstones increases with age, particularly after 40.
- Sex: Women are more likely to develop gallstones than men, possibly due to estrogen affecting cholesterol levels and gallbladder motility.
- Genetics: A family history of gallstones can increase your risk.
- Certain Medical Conditions: Conditions like Crohn’s disease, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and some autoimmune diseases can play a role.
- Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) and Oral Contraceptives: These can increase cholesterol levels in bile